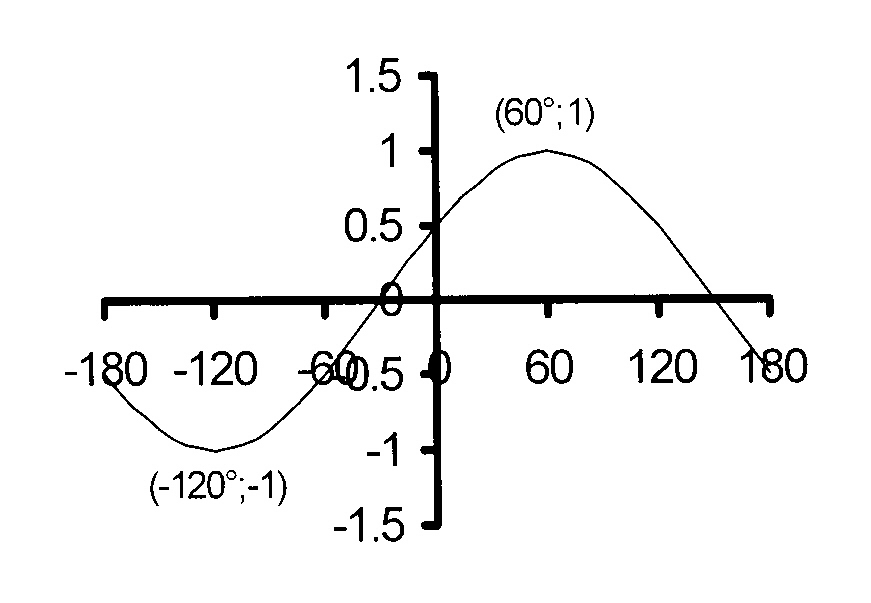$$ \hspace*{2 mm}\mathrm{1.1\kern3mmy = 2\ sin\ x\ − 1\kern2mm\ } $$
Vertical translation : q = minus; 1 and
The graph oscillates about y = minus; 1.
amplitude = 2
maximum = 2 − 1 = 1
minimum = − 2 − 1 = − 3
Period = 360°
The maximum is reached
at x = 90° and x = -270°
The minimum is reached
x = − 90° and x = 270°
 [ Q 1.1 ]
[ Q 1.1 ]
$$ \hspace*{2 mm}\mathrm{1.2\kern3mmy = 1 − 2 sin\ x\kern2mm\ } $$
Vertical translation : q = 1 and
the graph oscillates about y = 1.
amplitude = 2
maximum = 3
minimum = − 1
Period = 360°
The maximum is reached
at x = − 270° and x = 90°
The minimum is reached
at x = −270° and x = 90°
 [ Q 1.2 ]
[ Q 1.2 ]
$$ \hspace*{2 mm}\mathrm{1.3\kern3mmy = 2\ cos\ x\ − 1\kern2mm\ } $$
Vertical translation : q = − 1 and
the graph oscillates about y = − 1.
amplitude = 2
maximum = 1
minimum = − 3
Period = 360°
The maximum is reached
at x = − 360°; x = 0° and x = 360°
The minimum is reached
at x = −180° and x = 180°
 [ Q 1.3 ]
[ Q 1.3 ]
$$ \hspace*{2 mm}\mathrm{1.4\kern3mmy = 1 − 2\ cos\ x\kern2mm\ } $$
Vertical translation : q = 1 and
the graph oscillates about y = 1.
amplitude = 2
maximum = 3
minimum = − 1
Period = 360°
The maximum is reached
at x = − 180° and x = 180°
The minimum is reached
at x = −360°; x = 0° and x = 360°
 [ Q 1.4 ]
[ Q 1.4 ]
$$ \hspace*{2 mm}\mathrm{1.5\kern3mmy = sin\ (x − 30°)\kern2mm\ } $$
Vertical translation : q = 0 and
the graph oscillates about y = 0, the X-axis.
amplitude = 1
maximum = 1
minimum = − 1
Period = 360°
The maximum is reached
at x = − 240° and x = 120°
The minimum is reached
at x = −60°; x = 0° and x = 300°
 [ Q 1.5 ]
[ Q 1.5 ]
$$ \hspace*{2 mm}\mathrm{1.6\kern3mmy = sin\ (x + 60°)\kern2mm\ } $$
Vertical translation : q = 0 and
the graph oscillates about y = 0, the X-axis.
amplitude = 1
maximum = 1
minimum = − 1
Period = 360°
The maximum is reached
at x = − 330° and x = 300°
The minimum is reached
at x = −150°; x = 210°
 [ Q 1.6 ]
[ Q 1.6 ]
$$ \hspace*{2 mm}\mathrm{1.7\kern3mmy = cos\ (x − 60°)\kern2mm\ } $$
Vertical translation : q = 0 and
the graph oscillates about y = 0, the X-axis.
amplitude = 1
maximum = 1
minimum = − 1
Period = 360°
The maximum is reached
at x = − 300° and x = 60°
The minimum is reached
at x = −120°; x = 240°
 [ Q 1.7 ]
[ Q 1.7 ]
$$ \hspace*{2 mm}\mathrm{1.8\kern3mmy = cos\ (x + 30°)\kern2mm\ } $$
Vertical translation : q = 0 and
the graph oscillates about y = 0, the X-axis.
amplitude = 1
maximum = 1
minimum = − 1
Period = 360°
The maximum is reached
at x = − 30° and x = 330°
The minimum is reached
at x = −210°; x = 150°
 [ Q 1.8 ]
[ Q 1.8 ]
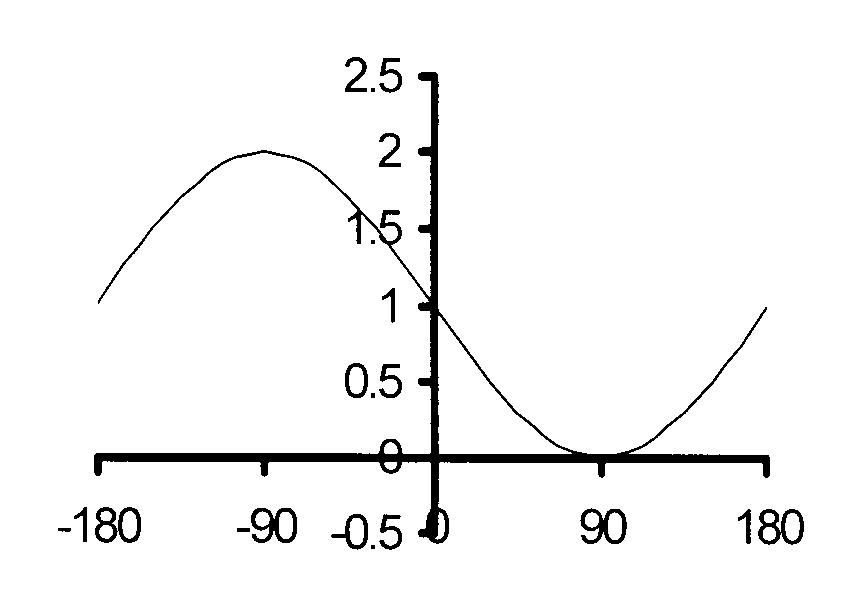
$$ \hspace*{2 mm}\mathrm{1.9\kern3mmy = 1 − sin x\kern2mm\ } $$
Vertical translation : q = 1 and
the graph oscillates about y = 1.
amplitude = 1
maximum = 2
minimum = 0
Period = 360°
The maximum is reached at x = − 90°
The minimum is reached at x = 90°
 [ Q 1.9 ]
[ Q 1.9 ]
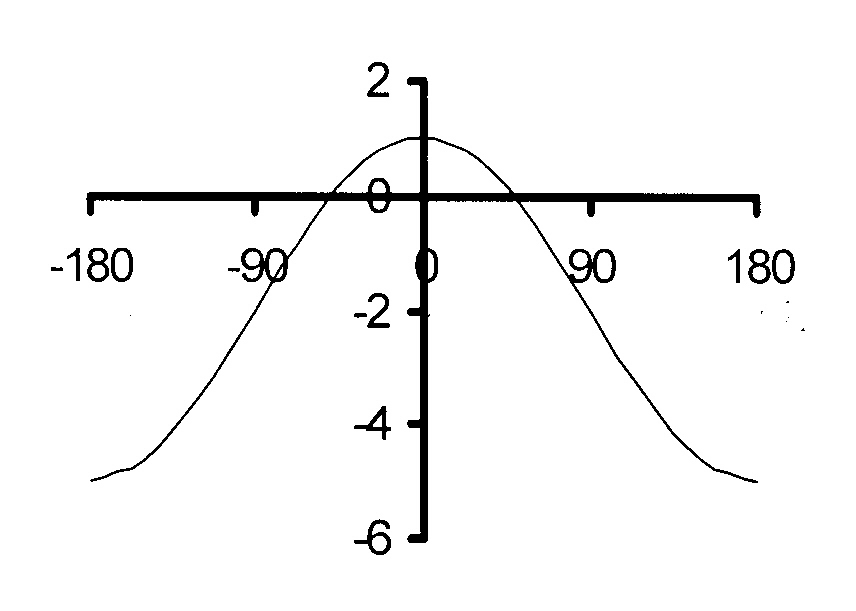
$$ \hspace*{2 mm}\mathrm{1.10\kern3mmy = 3\ cos\ x\ − 2\kern2mm\ } $$
Vertical translation : q = − 2 and
the graph oscillates about y = −2.
amplitude = 3
maximum = 3 × 1 − 2 = 1
minimum = 3 × −1 − 2 = −5
Period = 360°
The maximum is reached at x = 0°
The minimum is reached
at x = − 180° and x = 180°
 [ Q 1.1 ]
[ Q 1.1 ]
$$ \hspace*{2 mm}\mathrm{1.11\kern3mmy = sin\ (x − 30°)\kern2mm\ } $$
Vertical translation : q = 0 and
the graph oscillates about y = 0, the X-axis.
amplitude = 1
maximum = 1
minimum = −1
Period = 360°
The maximum is reached at x = 60°
The minimum is reached at x = − 120°
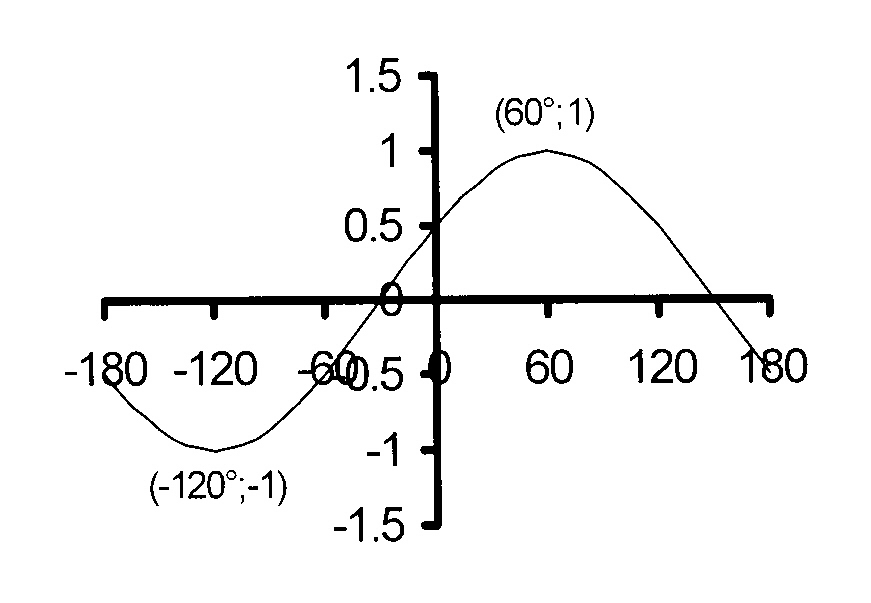 [ Q 1.11 ]
[ Q 1.11 ]
nr11M54sctg.html#qtrg0110
$$ \hspace*{2 mm}\mathrm{1.12\kern3mmy = cos\ (2x − 60°)\kern2mm\ } $$
$$ \hspace*{12 mm}\mathrm{y = cos\ 2(x − 30°)\kern2mm\ } $$
Vertical translation : q = 0 and
the graph oscillates about y = 0, the X-axis.
amplitude = 1
maximum = 1
minimum = −1
$$ \hspace*{9 mm}\mathrm{Period\ = \Big(\frac{360}{2}\Big)^{°} = 180°\kern2mm\ } $$
The maximum is reached
at x = −150° and x = 30°
The minimum is reached
at x = − 60° and x = 120°
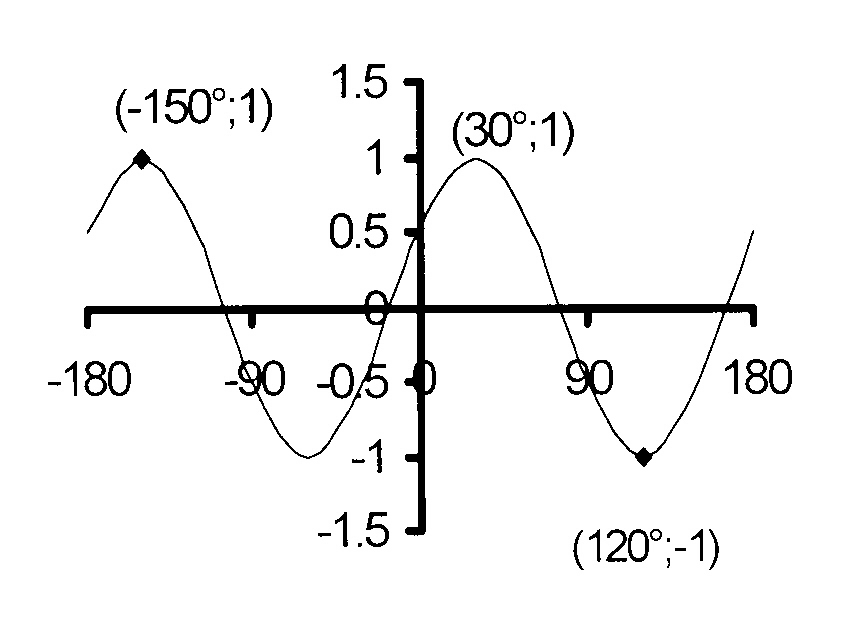 [ Q 1.12 ]
[ Q 1.12 ]
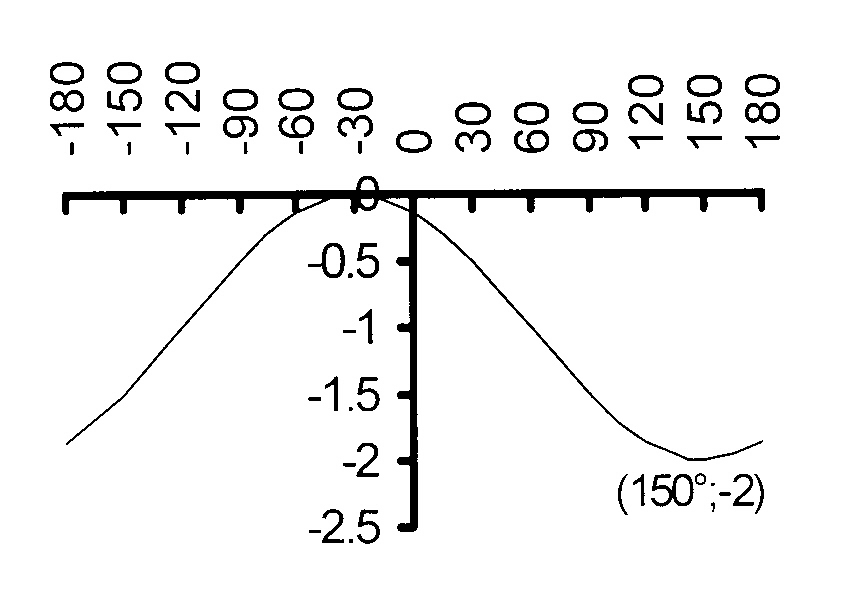
$$ \hspace*{2 mm}\mathrm{1.13\kern3mmy = cos\ (x + 30°)\ − 1\kern2mm\ } $$
Vertical translation : q = − 1 and
the graph oscillates about y = −1.
amplitude = 1
maximum = 1 − 1 = 0
minimum = −1 −1 = −2
k = 1 and period = 360°
Horizontal translation : p = 30° to the left
The maximum is reached at x = −30°
The minimum is reached at x = 150°
 [ Q 1.13 ]
[ Q 1.13 ]
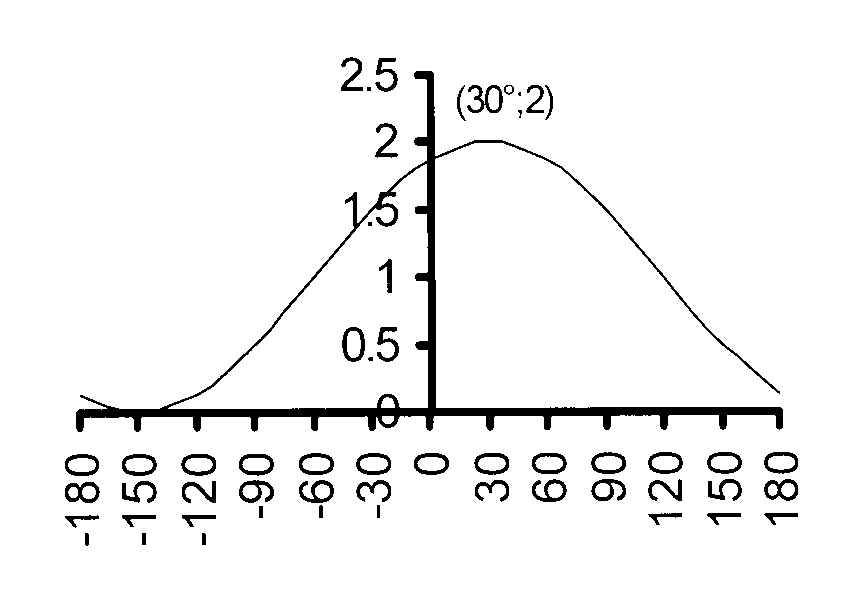
$$ \hspace*{2 mm}\mathrm{1.14\kern3mmy = sin\ (x + 60°)\ + 1\kern2mm\ } $$
Vertical translation : q = 1 and
the graph oscillates about y = 1.
amplitude = 1
maximum = 1 + 1 = 2
minimum = 1 − 1 = 0
k = 1 and period = 360°
Horizontal transtion : p = 60° to the left
The maximum is reached at x = 30°
The minimum is reached at x = −150°
 [ Q 1.14 ]
[ Q 1.14 ]
$$ \hspace*{2 mm}\mathrm{1.15\kern3mmy = tan\ x\kern2mm\ } $$
Asimptotes at x = -90° and x = 90°
Period = 180°
tan x = 1 at x = -135°; x = 45°.
tan x = − 1 at x = -45° and at x = 135°
Graph is increasing.
 [ Q 1.15 ]
[ Q 1.15 ]
$$ \hspace*{2 mm}\mathrm{1.16\kern3mmy = tan\ x +\ 1\kern2mm\ } $$
Asimptotes at x = -90° and x = 90°
Period = 180°
Vertical translation : q = 1
tan x = 1 at x = 0°.
Graph is increasing.
 [ Q 1.16 ]
[ Q 1.16 ]
$$ \hspace*{2 mm}\mathrm{1.17\kern3mmy = tan\ (x + 30°)\kern2mm\ } $$
Asimptotes at x = -120° and x = 60°
Period = 180°
Vertical translation : q = 0
Horizontal transtion : p = 30° to the left
tan x = 1 at x = −165° ; x = 15°.
Graph is increasing.
 [ Q 1.17 ]
[ Q 1.17 ]
$$ \hspace*{2 mm}\mathrm{1.18\kern3mmy = tan\ 2x\kern2mm\ } $$
Asimptotes at x = -45° and x = 45°
Period = 90°
Vertical translation : q = 0
Horizontal transtion : p = 0°
tan x = 1 at x = &inus;1650° ; x = 150°.
Graph is increasing.
 [ Q 1.18 ]
[ Q 1.18 ]
2.1 The graph of y = a sin k(x + p)
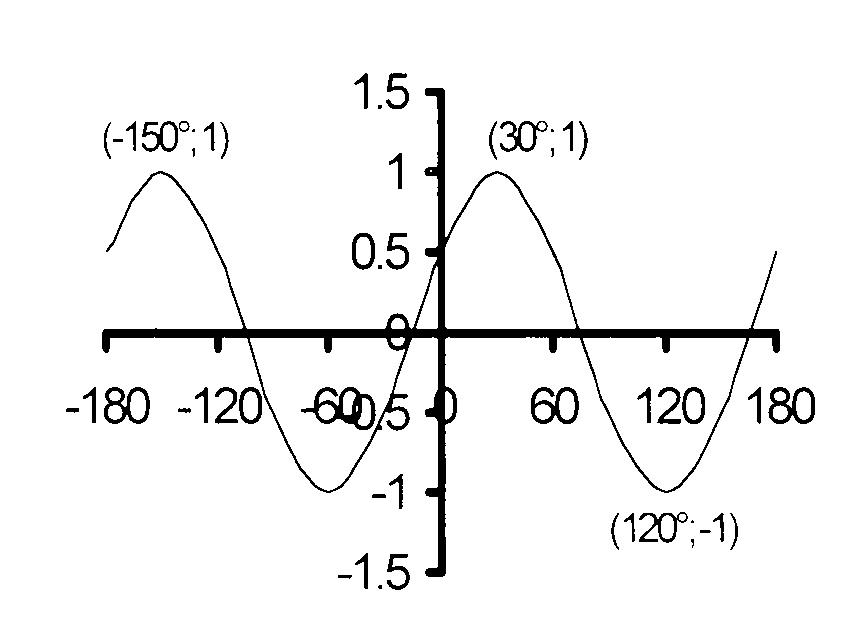 [ A 2.1 ]
[ A 2.1 ]
$$ \hspace*{2 mm}\mathrm{2.1\kern3mmy = a\ sin\ k(x + p)\ +\ q\kern2mm\ } $$
The graph oscillates about y = 0, the
X-axis and thus q = 0..
Amplitude = 1 so that a = 1.
$$ \hspace*{9 mm}\mathrm{period\ = 180°\ and\ k = \Big(\frac{360°}{180°}\Big) = 2\kern2mm\ } $$
Horizontal translation is 30° to the left; p = +30°
Equation : y = 1.sin 2x + 30°
= sin 2(x + 15)°
[ Q 2.1 ]
$$ \hspace*{2 mm}\mathrm{2.2\kern3mmy = a\ cos\ k(x + p)\ +\ q\kern2mm\ } $$
The graph oscillates about y = 0, the
X-axis and thus q = 0..
Amplitude = 1 so that a = 1.
$$ \hspace*{9 mm}\mathrm{period\ = 120°\ and\ k = \Big(\frac{360°}{120°}\Big) = 3\kern2mm\ } $$
Horizontal translation is 30° to the right; p = − 30°
Equation : y = 1.sin 2x + 30°
= sin 2(x + 15)°
[ Q 2.2 ]
$$ \hspace*{2 mm}\mathrm{2.3\kern3mmy = a\ sin\ k(x + p)\ +\ q\kern2mm\ } $$
The graph oscillates about y = 0, the
X-axis and thus q = 0.
Amplitude = 2 so that a = 2.
$$ \hspace*{9 mm}\mathrm{period\ = 120°\ and\ k = \Big(\frac{360°}{120°}\Big) = 3\kern2mm\ } $$
At A(20° ; 0) : 3(20° + p) = 0°
60° + 3p = 0°
p = − 20°
Equation : y = 2.sin 3(x − 20°)
= 2 sin 3(x − 20)°
[ Q 2.3 ]
$$ \hspace*{2 mm}\mathrm{2.4\kern3mmy = a\ cos\ k(x + p)\ +\ q\kern2mm\ } $$
The graph oscillates about y = 0, the
X-axis and thus q = 0..
Amplitude = 3 and the graph is a cosine graph
so that a = −3.
$$ \hspace*{9 mm}\mathrm{period\ = 180°\ and\ k = \Big(\frac{360°}{180°}\Big) = 2\kern2mm\ } $$
At A(15° ; 0) : 2(15° + p) = 90°
30° + 2p = 90°
p = 30°
Equation : y = − 3 cos 2(x + 30°)
= − 3 cos 2(x + 30)°
[ Q 2.4 ]
$$ \hspace*{2 mm}\mathrm{2.5\kern3mmy = a\ sin\ k(x + p)\ +\ q\kern2mm\ } $$
The graph oscillates about y = − 2, the
and thus q = − 2.
Amplitude = 3 so that a = 3.
Period = 360° and k = 1
There is no horizontal translation and p = 0
Equation : y = 3 sin (x + 0°) − 2
= − 3 sin x − 2
[ Q 2.5 ]
$$ \hspace*{2 mm}\mathrm{2.6\kern3mmy = a cos k(x + p) + q\kern2mm\ } $$
The graph oscillates about y = − 2, the
and thus q = − 2.
Amplitude = 3 so that a = 3.
$$ \hspace*{9 mm}\mathrm{period\ = 180°\ and\ k = \Big(\frac{360°}{180°}\Big) = 2\kern2mm\ } $$
There is no horizontal translation and p = 0°
Equation : y = 3 cos 2(x + 0°) − 2
= 3 cos 2x − 2
[ Q 2.6 ]

A(− 150°;0); B(30°;0);C(0;− 0,5)
[ Q 3.1 ]
$$ \hspace*{2 mm}\mathrm{3.2\kern3mmperiod = 360°\kern2mm\ } $$
[ Q 3.2 ]
$$ \hspace*{2 mm}\mathrm{3.3\kern3mmsin\ (x - 30°) = cos\ 2x\kern2mm\ } $$
$$ \hspace*{29 mm}\mathrm{= sin\ (90° − 2x)\kern2mm\ } $$
$$ \hspace*{17 mm}\mathrm{x − 30° = 2x + n.360°\kern2mm\ } $$
$$ \hspace*{26 mm}\mathrm{x = 40° + n.120°;\ \ n \isin Z\kern2mm\ } $$
$$ \hspace*{33 mm}\mathrm{\bold{OR}\kern2mm\ } $$
$$ \hspace*{17 mm}\mathrm{x − 30° = 180° − (90° − 2x) + n.360°\kern2mm\ } $$
$$ \hspace*{17 mm}\mathrm{x − 30° = 180° − 90° + 2x + n.360°\kern2mm\ } $$
$$ \hspace*{23 mm}\mathrm{− x = 120° + n.360°\kern2mm\ } $$
$$ \hspace*{24 mm}\mathrm{ x = −120° − n.360°\kern2mm\ } $$
Solution : x = 40°−1.120° ; 40° + 0.120° ;
x = 40° + 1.120° and − 120° − 0.360°;
Solution : x = − 80°(E); 40°(F); 160°(G) ; − 120°(D)
[ Q 3.3 ]
$$ \hspace*{2 mm}\mathrm{3.4\kern3mmf(x) < − 0,5\ \ if\ − 120° < x < 0°\kern2mm\ } $$
[ Q 3.4 ]
$$ \hspace*{2 mm}\mathrm{3.5\kern3mmf(x) ≥ 0,5\ \ if\ 60° ≤ x ≤ 180°\kern2mm\ } $$
[ Q 3.5 ]
4.1 f: amplitude = 2 and thus a = 2
The cosine graph reaches 0 at 60° instead
of at 90° so that the graph is shifted 30° to
the left and thus b = 30°
The sine graph, g, oscillates about y = 1 so
that c = 1
$$ \hspace*{8 mm}\mathrm{period = 180°\ and\ thus\ d = \Big(\frac{360°}{180°}\Big) = 2\kern2mm\ } $$
[ Q 4.1 ]
$$ \hspace*{2 mm}\mathrm{4.2\kern3mmf(x) = 2\ cos\ (x − 30°)\kern2mm\ } $$
$$ \hspace*{10 mm}\mathrm{f(0) = 2\ cos\ (0 + 30°)\kern2mm\ } $$
$$ \hspace*{16 mm}\mathrm{= 2\ cos\ 30°\kern2mm\ } $$
$$ \hspace*{16 mm}\mathrm{= 2\Big(\frac{\sqrt3}{2}\Big) = \sqrt3\kern2mm\ } $$
[ Q 4.2 ]
4.3.1 f: x = 45° and x = −135°
[ Q 4.3.1 ]
4.3.2 f and g intersect at (−90° ; 1) and
at (13,5° ; 1,45): hence the solution :
−90° ≤ x ≤ 13,5°
[ Q 4.3.2 ]
4.4 f(x) reaches its maximum at − 30°.
The axis is shifted 30° to the left,
i.e. the graph is shifted 30° to the right
and p = 30°
$$ \hspace*{10 mm}\mathrm{f(x) = 2 cos (x − 30°)\kern2mm\ } $$
$$ \hspace*{10 mm}\mathrm{f(x) = 2 cos (x + 30° − 30°)\kern2mm\ } $$
$$ \hspace*{10 mm}\mathrm{f(x) = 2 cos x\kern2mm\ } $$
[ Q 4.4 ]
5.1 f: amplitude = 1 and thus a = 1
The cosine graph reaches 1 at 30° in stead
of at 0° so that the graph is shifted 30° to
the right and thus b = −30°
The sine graph, g, has a period = 360°
so that c = 1
[ Q 5.1 ]
$$ \hspace*{2 mm}\mathrm{5.2.1\kern3mmRange\ :\ −0,5 \le y \le 1\kern2mm\ } $$
[ Q 5.2.1 ]
$$ \hspace*{2 mm}\mathrm{5.2.2\kern3mm30° < x \le; 90°\kern2mm\ } $$
[ Q 5.2.2 ]
$$ \hspace*{2 mm}\mathrm{5.2.3\kern3mmRange−90° ≤ x ≤ −60°\ \ and\ \ x = 0°\kern2mm\ } $$
[ Q 5.2.3 ]
$$ \hspace*{2 mm}\mathrm{5.3\kern3mmcos\ (x − 30°)\ =\ sin\ x\kern2mm\ } $$
$$ \hspace*{31 mm}\mathrm{= cos\ (90° − x)\kern2mm\ } $$
$$ \hspace*{16 mm}\mathrm{\therefore x − 30° = 90° − x + n\bold{.}360°\ \kern3mm\ n ∈ Z\kern2mm\ } $$
$$ \hspace*{23 mm}\mathrm{\therefore 2x = 120° + n\bold{.}360°\kern2mm\ } $$
$$ \hspace*{25 mm}\mathrm{\therefore x = 60° + n\bold{.}180°\kern2mm\ } $$
$$ \hspace*{25 mm}\mathrm{\therefore x = 60°\kern2mm\ } $$
If g(x) > f(x) then 60° < x ≤ 90°
[ Q 5.3 ]
5.4 The graph of g(x) is shifted 60° to the
left and therefore x changes to x + 60°
$$ \hspace*{10 mm}\mathrm{g(x) = sin x\kern2mm\ } $$
$$ \hspace*{10 mm}\mathrm{h(x) = sin (x + 60°)\kern2mm\ } $$
[ Q 5.4 ]
5.5 f(x) must be shifted 60° to the right
to become g(x).
[ Q 5.5 ]
6.1 Amplitude = 2 and hence c = 2 and
period = 360° and thus d = 1.
[ Q 6.1 ]
6.2 Amplitude = 1 and hence a = 1;
f(60°) = 1 and thus the graph is shifted
60° to the right so that b = − 60°
[ Q 6.2 ]
6.3 Range : − 2 ≤ y ≤ 2
[ Q 6.3 ]
6.4 −120° ≤ x ≤ − 30°
[ Q 6.4 ]
6.5 The Y-axis is shifted 30° to the left so
that the original sine graph was shifted
30° to the right and thus x changed to x − 30°
y = 2 sin x became y = 2 sin (x − 30°).
[ Q 6.5 ]
7.1 The graph of sin x = 0 at 0°
g(x) = 0 at − 30°. g(x) was shifted 30° to
the left and thus b = 30°.
[ Q 7.1 ]
7.2 Period = 360°
[ Q 7.2 ]
7.3 f(x) − g(x) = 0 at x = − 150° and
x = 30°:
[ Q 7.3 ]
7.4.1 sin (90° − x) = cos x, thus f(x) > g(x)
x ∈ (− 150° ; 30°)
[ Q 7.4.1 ]
7.4.2 For f(x)
.g(x) < 0, f(x) and g(x) must have
opposite signs. f(x) < 0 if x < − 90° and
g(x) < 0 if x < − 30°. Thus f(x) and g(x) have
opposite signs if −90° < x < −30°.
Thus f(x)
.g(x) < 0 if −90° < x < −30°.
[ Q 7.4.2 ]
7.4.3 f(x)
.g(x) ≥ 0 if −180° ≤ x ≤ −90° and
−30° ≤ x ≤ 90°.
[ Q 7.4.3 ]
7.5 f(x) has a minimum of − 1 and a maximum
of 1. All y-values becomes 3 greater,
therefore the range becomes
-1+3 ≤ y ≤ 1+3, i.e. 2 ≤ y ≤ 4.
[ Q 7.5 ]
7.6 f(x) is shifted 3 units downwards, so that
y = 0 − 3 = − 3. p(x) = cos x − 3
[ Q 7.6 ]
7.7 f(x) is shifted 30° to the left, so that
p = 30°. Thus q(x) = cos (x − 30°)
[ Q 7.7 ]